BECE 2003 Social Studies Past Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. Countries in North Africa are noted for the production of
Solution: North African countries, like Libya and Algeria, are major producers of crude oil, a key economic resource in the region.
2. Using a scale of 1:100,000 find the actual distance between two towns which are 4.5 centimetres apart on a map
Solution: Scale 1:100,000 means 1 cm = 100,000 cm = 1 km. Thus, 4.5 cm = 4.5 km = 4 km 500 m.
3. The revolution of the earth results in
Solution: The Earth’s revolution around the sun causes the four seasons due to the tilt of its axis, affecting sunlight distribution.
4. The most suitable physical feature for the construction of a dam is a
Solution: A gorge, with its narrow, steep-sided valley, is ideal for dam construction, as it requires less material and provides strong support.
5. A football match between Ghana (Longitude 0°) and Nigeria (Longitude 15°E) start in Lagos at 4 o’clock pm. At what time will the telecast of the match start in Ghana?
Solution: Nigeria is 15°E, one hour ahead of Ghana (0°). A 4 pm start in Lagos corresponds to 3 pm in Ghana.
6. Which of the following is a chemically formed sedimentary rock?
Solution: Potash is a chemically formed sedimentary rock, deposited through evaporation of mineral-rich water, unlike granite (igneous) or coal and lignite (organic).
7. Axim in the Western Region of Ghana is influenced by the
Solution: Axim, on Ghana’s coast, is influenced by the South-West Monsoon winds, which bring rainfall during the wet season.
8. The following are instruments used in measuring the elements of the weather and climate except
Solution: Clinometers measure angles of slope, not weather elements, unlike barometers (pressure), thermometers (temperature), and anemometers (wind speed).
9. How many times in a year is the sun vertically overhead at the equator?
Solution: The sun is vertically overhead at the equator twice a year, during the March and September equinoxes.
10. The conventional sign 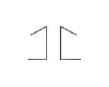
Solution: The 
11. Which of the following groups is not Ga-Adangme?
Solution: The Krobo, Kpone, and Osudoku are Ga-Adangme groups, but Takla is not a recognized Ga-Adangme ethnic group.
12. The beast of burden which was used to increase the volume of the Trans-Saharan Trade was the
Solution: Camels, known as “ships of the desert,” were critical for transporting goods across the Sahara, boosting the Trans-Saharan Trade.
13. The insect responsible for spreading river blindness is the
Solution: The simulium fly (black fly) transmits river blindness (onchocerciasis) through its bite, prevalent in riverine areas.
14. Which of the following ethnic groups celebrates the Kundum festival?
Solution: The Kundum festival is celebrated by the Nzema and Ahanta people in the Western Region, marking the harvest season.
15. People running away from Liberia because of the war to stay at Budumburam near Accra become in Ghana
Solution: Liberians fleeing war to Budumburam camp in Ghana are classified as refugees, seeking safety from conflict.
16. Government of the people, by the people and for the people is referred to as
Solution: Democracy, as defined by Abraham Lincoln, is a government system where power derives from the people’s participation and consent.
17. Until independence the Coat-of-Arms of the Gold Coast (Ghana) was
Solution: The colonial Gold Coast Coat-of-Arms featured an elephant and a palm tree, symbolizing the region’s resources.
18. Ghana’s earth satellite station is located in Greater Accra region at
Solution: Ghana’s satellite earth station is located at Kuntunse in the Greater Accra Region, facilitating telecommunications.
19. Gold in ancient Ghana was mined at
Solution: Wangara was a major gold-mining region in ancient Ghana, contributing to its wealth and trade.
20. Which of the following agencies cater for the welfare of women and children in the country?
Solution: The NCWD focuses on promoting the welfare and development of women and children in Ghana.
21. The Gonja under the leadership of Ndewura Jakpa migrated from
Solution: The Gonja, led by Ndewura Jakpa, migrated from the Mali Empire region to their current location in northern Ghana.
22. Which of the following personalities was not a member of the Convention People’s Party
Solution: Dr. K. A. Busia was a leader of the opposition United Party, not a member of the CPP, unlike the others listed.
23. The Fante Confederation agreed to have an assembly at
Solution: The Fante Confederation, formed in 1868, established its assembly at Mankesim, a significant cultural and political center.
24. Which of the following was the immediate cause of the 1948 disturbances in Ghana?
Solution: The shooting of three ex-servicemen during a march to Osu Castle on February 28, 1948, sparked the 1948 riots in Ghana.
25. The first political party which was formed in Ghana in 1947 was the
Solution: The UGCC, formed in 1947, was the first political party in Ghana, advocating for self-government.
26. The Aborigines’ Rights Protection Society was formed in the Gold Coast to protect
Solution: The Aborigines’ Rights Protection Society, formed in 1897, aimed to protect Gold Coast lands and minerals from British control.
27. Which of the following is not an ethnic group in Ghana?
Solution: Hausa is a linguistic and cultural group found in Ghana, but not a distinct ethnic group like Dagomba, Gonja, or Fante.
28. The date AD 1852 falls within the
Solution: AD 1852 is in the 19th century (1801–1900).
29. Which of the following political parties advocated for federalism in Ghana in 1957?
Solution: The NLM, formed in 1954, advocated for a federal system of government to protect regional interests, particularly in Ashanti.
30. All the following people inherit patrilineally except the
Solution: The Asante inherit matrilineally through the mother’s line, unlike the Adangme, Ewe, and Ga, who follow patrilineal inheritance.
31. The Second World War was fought between
Solution: The Second World War occurred from 1939 to 1945, involving major global powers.
32. Which of the following countries is the largest producer of rice in the world?
Solution: China is the world’s largest rice producer, accounting for a significant portion of global output.
33. The leading producer of coal in Africa is
Solution: South Africa is Africa’s leading coal producer, with extensive mining operations supporting its energy sector.
34. The only country in West Africa which did not come under colonial rule is
Solution: Liberia, founded by freed American slaves, remained independent, avoiding European colonial rule.
35. In which of the following countries is Lake Nasser located
Solution: Lake Nasser, formed by the Aswan High Dam, is located in Egypt, extending into Sudan.
36. One of the reasons for the partition of West Africa by the Europeans was to
Solution: European powers partitioned West Africa to secure and protect their trade interests, particularly in resources and markets.
37. Non-permanent members of the Security Council of the United Nations Organization (UNO) hold office for a period
Solution: Non-permanent members of the UN Security Council serve two-year terms, as stipulated in the UN Charter.
38. Which of the following minerals is non-metallic?
Solution: Diamond is a non-metallic mineral, composed of carbon, unlike copper, bauxite, and manganese, which are metallic.
39. Harvested food crops are best preserved in
Solution: Silos provide airtight storage, protecting harvested crops like grains from pests and moisture, ensuring long-term preservation.
40. Which of the following organizations was the first to be formed?
Solution: The League of Nations, formed in 1920, predates the UNO (1945), OAU (1963), and ECOWAS (1975).
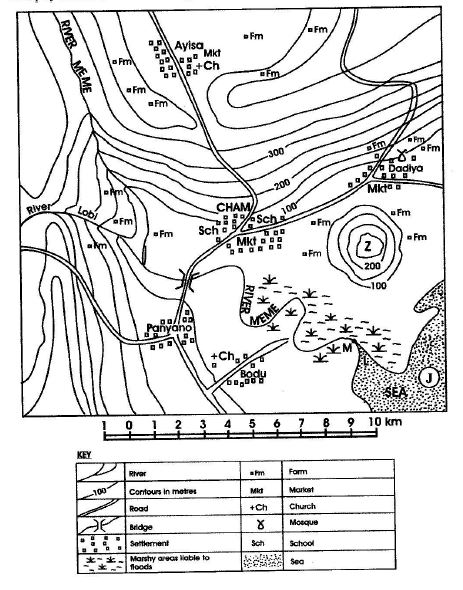
1. 1. (a) State the
1. (i) Contour intervals in metres
(b) Name the features marked M, L, J and Z
(c)(i) What type of settlement is Dadiya?
(ii) Name any two crops which will grow well in the swampy areas of the map.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1. (a) (i) Contour intervals in metres: 50 metres
(ii) Direction of Dadiya from Panyano: North East or north eastern direction
(iii) Distance by road from the road junction of Panyano to the road junction to Cham: 5.1 km [or 5 km or 5.2 km]
(iv) Direction of flow River Meme: From north west to south east
(b) (i) M - mouth (of the river Meme)
(ii) L - estuary
(iii) J - island or sandbank
(iv) Z - knoll or conical hill
(c) (i)Type of settlement Dadiya is: Linear settlement
(ii) Crops which will grow well in the swampy areas: Rice, sugarcane
2.(a) Name three types of rainfall
(b) With the help of a diagram describe how any one type of rainfall is formed.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2.
(b) (i) Convectional:
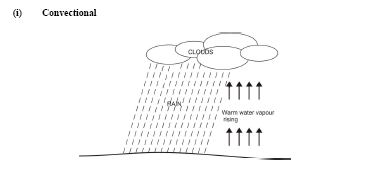
Warm water vapour rises (evaporates) from the surfaces of land and water bodies when they are heated.
The water vapour rises higher and higher into the atmosphere.
The higher it rises, the cooler it becomes.
When it gets into the upper layers of the atmosphere, it condenses to form cumulus clouds.
The cumulus clouds develop into cumulus congestus then into cumulonimbus clouds when cooling continues.
The cumulonimbus clouds condense further and fall as rain.
(Convectional rain is usually accompanied by thunder and lightning)
(ii) Relief or orographic:
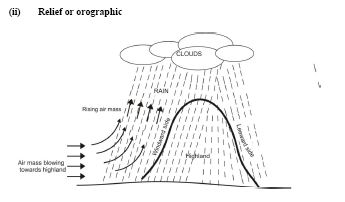
Air mass / wind blows towards a highland / mountain
The air mass is forced upwards on the windward side
The rising air cools (adiabatic cooling) and condenses to form cumulus clouds
The cumulus clouds develop into cumulus congestus then into cumulonimbus clouds as cooling continues
The cumulonimbus clouds condense further and fall as rain
The rain is heavier on the windward side than on the leeward side.
(iii) Cyclonic or frontal:
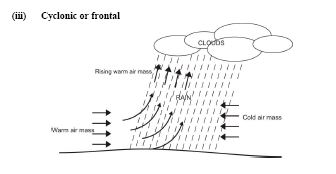
Two air masses (one warm, the other cold) meet and form a front.
The warmer air rises over the colder air, since it is lighter / has lower density
As the warm air continues to rise, it cools and condenses to form cumulus clouds
The cumulus clouds develop into cumulus congestus then into cumulonimbus clouds as cooling continues
The cumulonimbus clouds condense further and fall as rain
3. 3. (a) Name the three arms of Government
3. (b) State two functions of each of the three arms of Government
(c) Mention four sources of revenue for the district assemblies in Ghana.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3.(a) (i) The executive
(ii) The legislature
(iii) The judiciary
(b) (i) The Executive:
Formulation and implementation of state policies
Preparation and presentation of the national budget
General administration of the country
Implementing the decisions of Government
Signing of treaties on behalf of government
(ii) The Judiciary:
Interpreting the constitution and the laws of the state
Settling disputes and dispensing justice
Protection of human rights and freedoms
Judicial review - checking the constitutionality or otherwise of actions or other arms of government
(iii) The Legislature:
Making and amending laws for the country
Debating and approving (or rejecting) the national budget
Monitoring, evaluation and assessment of government policies
Impeachment of the president or his vice when necessary
Vetting of ministers who have been nominated by the presidency
(c) (i) Property rates
(ii) Districts assembly common fund
(iii) Licences fees
(iv) Loans/grants
(v) Royalties
(vi) Tolls (charges) for commercial activities
(vii) Court fines
(viii) Government grants
(ix) Income generation ventures / campaigns
(x) Donations from NGOs
4. 4. (a) Name four plantation farms and their locations in Ghana
4. (b) State four effects of plantation farming in Ghana
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4.(a) (i) Oil palm - Twifo, Benso, Kade, Juabeng, Kwae, Esiama
(ii) Mango, Citrus - Asebu, Somanya, Nsawam
(iii) Rubber - Benso, Bonsaso, Axim
(iv) Cocoa - Sefwi, Dunkwa, Mampong, Abirem, Tafo, Sankore
(v) Jute - Ejura
(vi) Pineapple - Nsawam
(vii) Cashew nuts - Wenchi
(b) (i) Positive effects:
They help to guarantee food sufficiency and security for the country
They help to provide employment for people
They help the country to earn foreign exchange through exports
They help to generate revenue for Ghana
They supply raw materials for processing / manufacturing industries
(ii) Negative effects:
They use up very large portions of land which could have been used for other purposes.
They destroy natural vegetation (forest trees and other plants)
They destroy game and wildlife
They could cause unemployment, where a few machines replace several people in working.
They may lead to land ownership problems, where the plantation stretches across more than one community
5. 5. (a) State any four aims of the United Nations Organization
5. (b) Explain two problems facing the United Nations Organization
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
5.(a) (i) To maintain world peace
(ii) To develop good relations among countries
(iii) To promote cooperation in solving the world’s problems
(iv) To encourage respect for human rights
(v) To prevent the recurrence of another world war
(b) (i) Financial difficulties - The UNO does not have enough funds to implement all its programmes effectively. This is partly due to the inability of some member states to pay their dues to the UNO regularly. The ever-growing world problems also put a huge strain on the limited funds of the organization
(ii) Political hindrances - Each of the five permanent members of the Security Council has what is referred to as ‘veto power’. With this power, they can block an action that the other states have agreed upon to pursue. As a result, the organization many times is unable to act in a certain way to achieve a desired result - simply because one permanent member has exercised her veto power to block the action, probably because it may not suit her.
(iii) Absence of regular peace-keeping troops - The UNO does not have regular (ever ready) troops for peace-keeping. So in case of a crisis situation, a lot of time could be wasted trying to assemble troops from various countries. This could cause delays in timely intervention, which could make the crisis situation worse.
(iv) Numerous socio-cultural difficulties - Several countries or regions of the world are faced with numerous socio-economic problems such as epidemics (fast-spreading disease), human rights abuses, educational difficulties, developmental difficulties, etc. The UNO is struggling to appropriately address these challenges.
(v) International crime and terrorism - The UNO is finding it quite difficult to cope with the rising cases of international crimes and terrorism, such as suicide bombings, hijacking of planes / ships, drug trafficking, etc.
(vi) Non-cooperation of some member states - Certain member states do not cooperate when it comes to certain issues, because they believe it does not favour them. Consequently, they may refuse to sign certain resolutions and / or may not abide by them, even when they sign. This sets back the mission of the UN.
6. 6. What five major problems face the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)?
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 6
6.(i) Financial difficulties - ECOWAS does not have enough funds to implement all its projects effectively. This is partly due to the inability of some member states to pay their dues to ECOWAS regularly. The ever-growing regional problems also put a huge strain on the limited funds of the community.
(ii) Large number of member states - Currently, in terms of member states, ECOWAS is the largest economic community in the world. Its large size creates serious challenges with policy-making and the practical implementation of economic integration.
(iii) Currency differences - There are at least eight different currencies used by member states of ECOWAS. This has significantly hampered the smooth economic integration among member countries.
(iv) Language barrier - Effective communication among members of the community is a problem due to the language differences among member states. There are three (3) official languages and hundreds of other indigenous / local languages.
(v) Influence of Colonial Masters - Some member states of ECOWAS show very little interest and commitment. This could partly be attributed to the fact that they still receive various forms of assistance from their colonial masters. This tends to make them more committed to their colonial master than the regional community, which negatively affects the prospects of ECOWAS’ success.
(vi) Membership of other economic groups - Certain ECOWAS members are also members of other economic groups. This causes those states to have divided loyalty, which makes them less committed to ECOWAS
(vii) Political Instability - The lack of political stability in the west African sub-region poses a great threat to the effectiveness of ECOWAS. The high incidence of coup d’états, tribal and religious conflicts, civil wars, etc., in the region is a serious drawback and strain to ECOWAS.